「Windows ACLs を利用して共有を設定する」の版間の差分
| 70行目: | 70行目: | ||
== | == <code>SeDiskOperatorPrivilege</code> 権限の付与 == | ||
<code> SeDiskOperatorPrivilege </code>権限を付与されたユーザーとグループのみが共有権限を設定できます。 | <code> SeDiskOperatorPrivilege </code>権限を付与されたユーザーとグループのみが共有権限を設定できます。 | ||
2019年2月26日 (火) 16:49時点における版
はじめに
Extended access control lists (ACL) enable you to set permissions on shares, files, and directories using Windows ACLs and applications. Samba supports shares using extended ACLs on: 拡張アクセス制御リスト(ACL)を使用すると、WindowsのACLおよびアプリケーションを使用して、共有、ファイル、およびディレクトリに対するアクセス許可を設定できます。Sambaは、以下で拡張ACLを使用して共有をサポートします。
- ドメインメンバ
- Active Directory (AD) ドメインコントローラ (DC)
- NT4 プライマリドメインコントローラ (PDC)
- NT4 バックアップドメインコントローラ (BDC)
- スタンドアローンホスト
拡張ACLの代わりに、POSIX ACLを使用して共有を設定できます。 詳細については、 POSIX ACLs を利用して共有を設定するを見てください。. {{#invoke:Message box|imbox}}
ホストの準備
共有を作成する前にSambaを設定する必要があります。 どのタイプのSambaサーバーが必要かに応じて、以下を参照してください:
- SambaをActive Directoryドメインメンバとして構成する
- SambaをActive Directoryドメインコントローラとして設定する
- Setting up Samba as an NT4 PDC (Quick Start)
- Setting up Samba as an NT4 BDC
- Setting up Samba as a Standalone Server
ファイルシステムのサポート
共有が作成されるファイルシステムは、次のものをサポートしている必要があります。:
- ユーザーとシステムの
xattr名前空間。 - 拡張されてアクセスコントロールリスト (ACL).
For further details, see File system support.
拡張ACL(Access Control List)をサポートする共有を作成するには、 smbd サービスがACLサポートを有効にして構築されている必要があります。 Active Directory(AD)ドメインコントローラ(DC)として機能するSambaホストは、拡張ACLサポートにより常に有効になっています。
To verify if Samba has been built with ACL support, enter:
# smbd -b | grep HAVE_LIBACL HAVE_LIBACL
If no output is displayed:
- Samba was built using the
--with-acl-support=noparameter. - The Samba
configurescript was unable to locate the required libraries for ACL support. For details, see Package Dependencies Required to Build Samba.
smb.conf ファイルで拡張ACLサポートを有効にする File
拡張アクセス制御リスト(ACL)を使って共有を設定するには、 smb.conf ファイルでサポートを有効にする必要があります。 拡張ACLサポートをグローバルに有効にするには、 smb.conf ファイルの [global] セクションに次の設定を追加します。
vfs objects = acl_xattr map acl inherit = yes store dos attributes = yes
{{#invoke:Message box|imbox}}
あるいは、特定の共有に対してのみ拡張ACLサポートを有効にするには、共有のセクションにパラメータを追加します。
For further details about the parameters, see the smb.conf(5) man page.
SeDiskOperatorPrivilege 権限の付与
SeDiskOperatorPrivilege 権限を付与されたユーザーとグループのみが共有権限を設定できます。
Domain Admins グループに権限を付与するには、次のように入力します。
# net rpc rights grant "SAMDOM\Domain Admins" SeDiskOperatorPrivilege -U "SAMDOM\administrator" Enter SAMDOM\administrator's password: Successfully granted rights.
{{#invoke:Message box|imbox}}
SeDiskOperatorPrivilege 特権が付与されているすべてのユーザーとグループを一覧表示するには、次のように入力します。
# net rpc rights list privileges SeDiskOperatorPrivilege -U "SAMDOM\administrator" Enter administrator's password: SeDiskOperatorPrivilege: BUILTIN\Administrators SAMDOM\Domain Admins
{{#invoke:Message box|imbox}}
To share the /srv/samba/Demo/ directory using the Demo share name:
- As the
rootuser, create the directory:
# mkdir -p /srv/samba/Demo/
- To enable other accounts than the domain administrator to set permissions on Windows, grant
Full control(rwx) to the user or group you granted theSeDiskOperatorPrivilegeprivilege. For example:
# chown root:"Domain Admins" /srv/samba/Demo/ # chmod 0770 /srv/samba/Demo/
- Add the
[Demo]share definition to yoursmb.conffile:
[Demo]
path = /srv/samba/Demo/
read only = no
- Further share-specific settings and file system permissions are set using the Windows utilities.
- {{#invoke:Message box|imbox}}
- Reload the Samba configuration:
# smbcontrol all reload-config
When you configure a share with extended access control lists (ACL) support, you set the share permissions using Windows utilities instead of adding parameters to the share section in the smb.conf file.
To set permissions and ACLs on the Demo share:
- Log on to a Windows host using an account that has the
SeDiskOperatorPrivilegeprivilege granted. e.g.SAMDOM\AdministratororSAMDOM\johnwherejohnis a member ofDomain Admins.
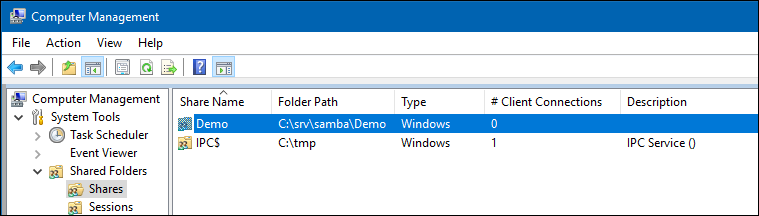
- Click
Start, enterComputer Management, and start the application.
- Select
Action/Connect to another computer.
- Enter the name of the Samba host and click
OKto connect the console to the host.
- Open the
System Tools/Shared Folders/Sharesmenu entry.
- Right-click to the share and select
Properties.
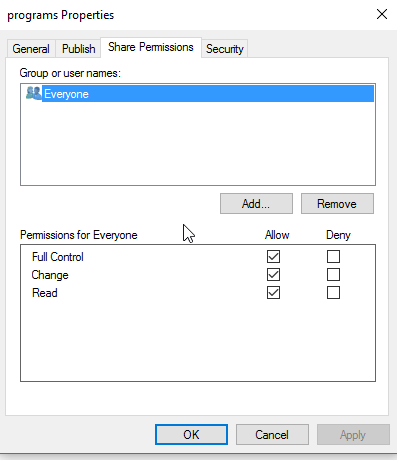
- Select the
Share Permissionstab and check the share permissions, you need to seeEveryone. For example:
- Samba stores share permissions in the
/usr/local/samba/var/locks/share_info.tdbdatabase.
- Select the
Securitytab.
- Click the
Editbutton and set the file system ACLs on the share's root directory. For example:
- For details about using the
SYSTEMaccount on a Samba share see The SYSTEM Account.
- For details where the ACLs are stored, see File System ACLs in the Back End.
- Click the
Addbutton.
- Click
Advancedbutton
- Click
Find Now
- Select a user or group from the list,
Domain Usersfor instance.
- Click
OK
- Click
OK
- Select permissions to grant,
Full controlfor instance.
- A windows security box should open, asking if you want to continue, Click
Yes
- If you check the list of
Group or user names, you should findDomain Userslisted
- Click
OKto close thePermissions for Demowindow.
- Click
OKto store the updated settings.
For further details about configuring share permissions and ACLs, see the Windows documentation.
Setting ACLs on a Folder
To set file system permissions on a folder located on a share that uses extended access control lists (ACL):
- Log on to a Windows host using an account that has
Full controlon the folder you want to modify the file system ACLs.
- Navigate to the folder.
- Right-click to the folder and select
Properties.
- Select the
Securitytab and click theEditbutton.
- Set the permission. For example:
- For details about using the
SYSTEMaccount on a Samba share see The SYSTEM Account.
- For details where the ACLs are stored, see File System ACLs in the Back End.
- Click
OKto close thePermissions for Folderwindow.
- Click
OKto store the updated settings.
For further details about setting ACLs, see the Windows documentation.
File System ACLs in the Back End
Samba stores the file system permissions in extended file system access control lists (ACL) and in an extended attribute. For example:
- To list the extended ACLs of the
/srv/samba/Demo/directory, enter:
# getfacl /srv/samba/Demo/ # file: srv/samba/Demo/ # owner: root # group: root user::rwx user:root:rwx group::--- group:root:--- group:domain\040users:rwx group:domain\040admins:rwx mask::rwx other::--- default:user::rwx default:user:root:rwx default:group::--- default:group:root:--- default:group:domain\040users:rwx default:group:domain\040admins:rwx default:mask::rwx default:other::---
- To list the
security.NTACLextended attribute of the/srv/samba/Demo/directory, enter:
# getfattr -n security.NTACL -d /srv/samba/Demo/ # file: srv/samba/Demo/ security.NTACL=0sBAAEAAAAAgAEAAIAAQC4zK0lHchKFvwXwbPR/h8P8sXMj5dNIT5QQuWsYwO3RAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAcG9zaXhfYWNsAEbGxuGu39MBuiZRk2pYxeL5ZWc4au0ikqRAk53MkjVd2b4quyk2WwcAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAEABJy0AAAA0AAAAAAAAADsAAAAAQUAAAAAAAUVAAAASSVmaZneO8cxOHk/9AEAAAEFAAAAAAAFFQAAAEklZmmZ3jvHMTh5P0oIAAACAMQABwAAAAALFACpABIAAQEAAAAAAAEAAAAAAAAUAAAAEAABAQAAAAAAAQAAAAAACxQA/wEfAAEBAAAAAAADAAAAAAALFACpABIAAQEAAAAAAAMBAAAAAAMkAP8BHwABBQAAAAAABRUAAABJJWZpmd47xzE4eT9KCAAAAAAkAP8BHwABBQAAAAAABRUAAABJJWZpmd47xzE4eT/0AQAAAAMkAL8BEwABBQAAAAAABRUAAABJJWZpmd47xzE4eT8BAgAA
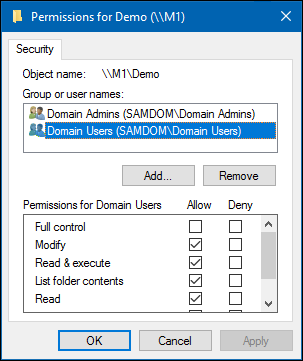
The previous example of file system ACLs and the extended attribute is mapped to the following Windows ACLs:
| Principal | Permissions | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Users (SAMDOM\Domain Users) | Modify, Read & execute, List folder contents, Read, Write | (This folder, subfolders and files) |
| Domain Admins (SAMDOM\Domain Admins) | Full control | (This folder, subfolders and files) |
- To get the ACL in a more readable form, enter:
# samba-tool ntacl get /usr/local/samba/var/locks/sysvol --as-sddl # O:BAG:SYD:PAI(A;OICIIO;WOWDGRGWGX;;;CO)(A;OICIIO;GRGX;;;AU)(A;;0x001200a9;;;AU)(A;OICIIO;GA;;;SY)(A;;0x001f01ff;;;SY)(A;OICIIO;WOWDGRGWGX;;;BA)(A;;0x001e01bf;;;BA)(A;OICIIO;GRGX;;;SO)(A;;0x001200a9;;;SO)
Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting, see: